- The clinical features of DKA are due to:
- Marked dehydration
- Acidosis
- Electrolyte disturbance
- Presenting signs and symptoms of DKA:
- Vomiting
- Polydipsia
- Polyuria
- Weakness
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Hyperventilation
- Dry mucus membranes
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension
- Disorientation
- Coma
- Underlying infection
- Repeat blood and urine test frequently
- Place patient in left lateral position
- Monitor fetal heart rate
- Check for evidence of infection
- If in coma/stupor O2 nasal cather.
- The increased risk of hypoglycemia during pregnancy occurs in:
-
- Early pregnancy; first trimester
- During sleep
- Patient with previous history of hypoglycemia
- Symptoms
-
- Tachycardia
- Tremor
- Hunger
- Pallor
- Dizziness
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Headache
- Paraesthesia
- Concentration & memory loss
- Confusion
- Somnolence
- Stupor, convulsions and coma
- Indication for IOL before 40 weeks
-
- Poor metabolic control
- Diabetic patient with vascular disease
- Poor compliance
- Premature stillbirth
- Progresing retinopathy
- Fetal reson as macrosome
Dette dokument er flaget "Muligt forældet"
Find siden via vejledninger
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Main and Danish guidelines by the web master
|
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute metabolic and obstetric emergency that can jeopardize both mother and fetus. Normally treated in ICU. Fetal mortality as high as 50%. Pregnant patient can develop DKA with glucose level less than 20 mg/dl.
Diagnostic criteria for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS)
Calculation: 2[measured Na (mEq/L)] + glucose (mg/dL)/18. Calculation: (Na+) - (Cl- + HCO3-) (mEq/L). See text for details. Copyright © 2006 American Diabetes Association From Diabetes Care Vol 29, Issue 12, 2006. Reprinted with permission from the American Diabetes Association. Additional Laboratory Findings Glucosuria Leukocytosis Ketonuria Elevated CPK Metabolic acidosis Elevated amylase Hyperosmolarity Elevated transaminase Hypokalemia Elevated BUN Hypomagnesemia Elevated Creatinine Hypophosphatemia Monitoring Serum glucose, serum ketones, arterial blood gas, creatinine, HCO2, serum electrolytes, anion gap, BUN, pulse oximetry, Urinary output Tabel II Protocol for the management of adult patients with HHS 
HHS diagnostic criteria: serum glucose >600 mg/dl, arterial pH >7.3, serum bicarbonate >15 mEq/l, and minimal ketonuria and ketonemia. Normal atory laboratory values vary; check local lab normal ranges for all electrolytes. IV: intravenous; SC: subcutaneous. * After history and physical exam, obtain capillary glucose and serum or urine ketones (nitroprusside method). Begin one liter of 0.9 percent NaCl over one hour and draw arterial blood gases, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, serum glucose, BUN, electrolytes, chemistry profile and creatinine levels STAT. Obtain electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, and specimens for bacterial cultures, as needed. Serum Na+ should be corrected for hyperglycemia (for each 100 mg/dl glucose >100 mg/dl, add 1.6 mEq to sodium value for corrected serum sodium value). Copyright © 2006 American Diabetes Association From Diabetes Care Vol 29, Issue 12, 2006. Reprinted with permission from the American Diabetes Association. Protocol for the management of adult patients with DKA 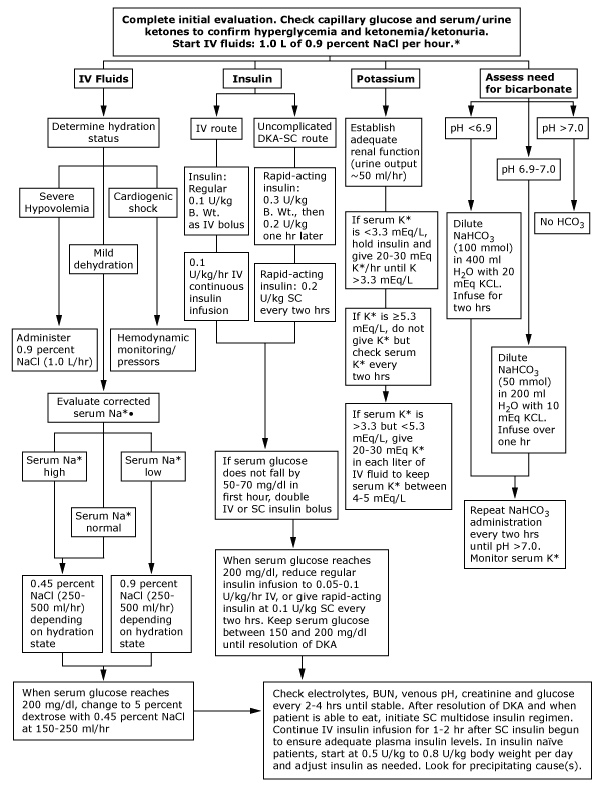
DKA diagnostic criteria: serum glucose >250 mg/dl, arterial pH <7.3, serum bicarbonate <18 mEq/l, and moderate ketonuria or ketonemia. Normal laboratory values vary; check local lab normal ranges for all electrolytes. IV: intravenous; SC: subcutaneous. * After history and physical exam, obtain capillary glucose and serum or urine ketones (nitroprusside method). Begin one liter of 0.9 percent NaCl over one hour and draw arterial blood gases, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, serum glucose, BUN, electrolytes, chemistry profile, and creatinine levels STAT. Obtain electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, and specimens for bacterial cultures, as needed. * Serum Na+ should be corrected for hyperglycemia (for each 100 mg/dl glucose >100 mg/dl, add 1.6 mEq to sodium value for corrected serum sodium value). American Diabetes Association From Diabetes Care Vol 29, Issue 12, 2006 Management of diabetes (1) Full diet (2) Calculate the total number of insulin units administered over 24 hours following stabilization.
One glass of apple juice and extra bread Less than 6 mmol before sleep give extra bread Unconscious Give 100 to 200 cc isotonic glucose or (20-50 cc 20%) and if difficult give Gluca Gen 1 mg im Elective delivery for poorly control diabetes before 38 weeks. Induction of labor before 40 week should be limited to those maternal or fetal complications that necessitate delivery before 40 weeks. Estimated fetal weight of 4500 or more cesarean delivery should be considered.
Feel free to mail me |